In previous article, we focused on Shadow image with Material Shadow library and today we come with cool animation with View using FloatingView animation library in Android. It can make the target view floating above the anchor view with cool animation.
You can see demo(FloatingView Animation) below:
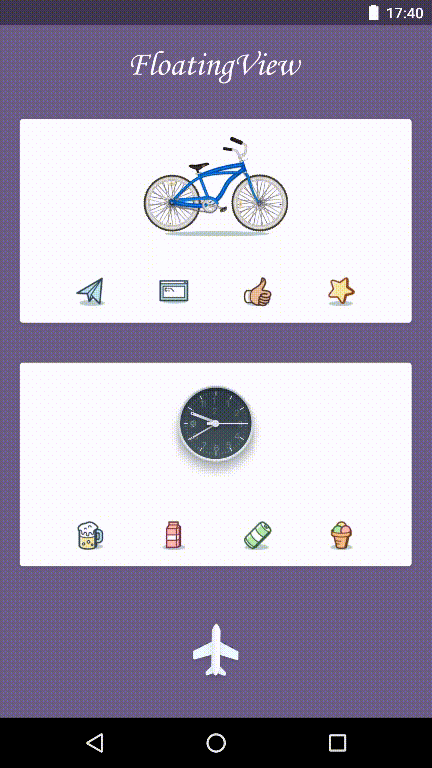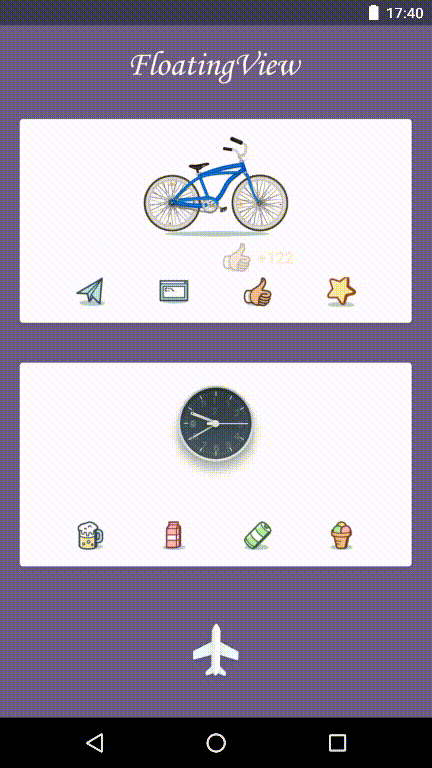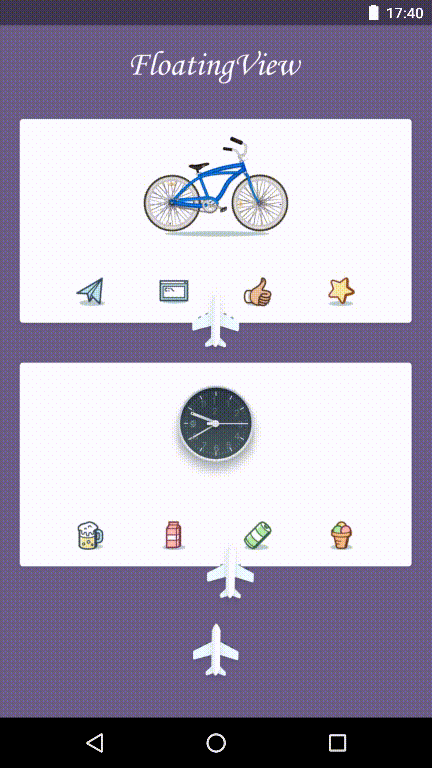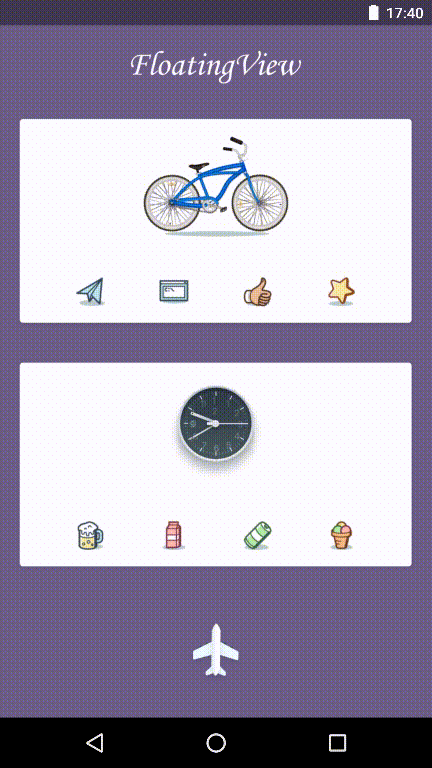
Let’s move on to implementation of FloatingView Animation:
Build gradle
First of all we need to add dependencies in build.gradle.
dependencies {
compile 'com.ufreedom.uikit:FloatingViewLib:1.0.2'
}
Create floating element
Use FloatingBuilder to create a FloatingElement
FloatingElement builder = new FloatingBuilder()
.anchorView(View)
.targetView(View)
.offsetX(int)
.offsetY(int)
.floatingTransition(FloatingTransition)
.build();
The use of FloatingBuilder can be configured to have:
- anchorView :Anchor, is you want to float animation in which View above
- target:Target, The view which you want to float
- offsetX:X direction of offset, unit PX
- offsetY: Y direction of offset, unit PX
- floatingTransition : Floating effect, the default is ScaleFloatingTransition
You can use this also : Use GIF in Android
[tmh_article_ads]
Create floating container
Finally, we create a Floating as a FloatingElement container, and then let your View fly up
Floating floating = new Floating(getActivity());
floating.startFloating(builder);
Customisation
Coordinates

Class Diagram

Floating Animation
Implementation of floating animation is very simple, you only need to implement the FloatingTransition interface.
public interface FloatingTransition {
public void applyFloating(YumFloating yumFloating);
}
In the applyFloating method, you can use Android Animation to do the animation, and then use the YumFloating to do Alpha , Scale, Translate, Rotate and other transformations. If you want to add the Facebook Rebound animation effect, you can use the SpringHelper, For example, ScaleFloatingTransition:
public class ScaleFloatingTransition implements FloatingTransition {
...
@Override
public void applyFloating(final YumFloating yumFloating) {
ValueAnimator alphaAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f, 0.0f);
alphaAnimator.setDuration(duration);
alphaAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
yumFloating.setAlpha((Float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue());
}
});
alphaAnimator.start();
SpringHelper.createWithBouncinessAndSpeed(0.0f, 1.0f,bounciness, speed)
.reboundListener(new SimpleReboundListener(){
@Override
public void onReboundUpdate(double currentValue) {
yumFloating.setScaleX((float) currentValue);
yumFloating.setScaleY((float) currentValue);
}
}).start(yumFloating);
}
}
If SpringHelper can not meet your needs, you can directly use the createSpringByBouncinessAndSpeed(double bounciness, double speed) or createSpringByTensionAndFriction(double tension, double friction) to create the Spring, and then use transition (Progress double, startValue float, endValue float) for numerical conversion
Floating Path Animation
The floating path animation is also very simple, such as CurveFloatingPathTransition, first you need to inherit from the BaseFloatingPathTransition class ,The difference is, you need to implement a getFloatingPath () method. Use Path in the getFloatingPath ()method to create the path you want to float, and then call FloatingPath.create (path, false) to return. For example, CurveFloatingPathTransition implementation:
public class CurveFloatingPathTransition extends BaseFloatingPathTransition {
...
@Override
public FloatingPath getFloatingPath() {
if (path == null){
path = new Path();
path.moveTo(0, 0);
path.quadTo(-100, -200, 0, -300);
path.quadTo(200, -400, 0, -500);
}
return FloatingPath.create(path, false);
}
@Override
public void applyFloating(final YumFloating yumFloating) {
ValueAnimator translateAnimator;
ValueAnimator alphaAnimator;
translateAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(getStartPathPosition(), getEndPathPosition());
translateAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
float value = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
PathPosition floatingPosition = getFloatingPosition(value);
yumFloating.setTranslationX(floatingPosition.x);
yumFloating.setTranslationY(floatingPosition.y);
}
});
...
}
}
Use Path to describe the path you want to float, and then in applyFloating (YumFloating yumFloating):
- Use
getStartPathPosition ()method to obtain the starting position of the path - Use
getEndPathPosition ()method to obtain the end position of the path - Use
getFloatingPosition(float progress)to get the position of the current progress
getFloatingPosition(float progress)method will return a PathPosition object, its properties x an y representing the current path animation x coordinates and Y coordinates.
Download this project
Hope you like this article.

Share your thoughts